Articulation / Pronunciation
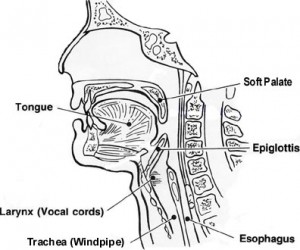 Articulation is the process by which sounds are formed when your tongue, jaw, teeth, lips and palate alter the air stream coming from your voice box. Articulation difficulties are usually characterized by substituting one sound for another (“wabbit” for “rabbit”), omitting a sound (“tar” for “star”) or distorting a sound (“ship” for “sip”).
Articulation is the process by which sounds are formed when your tongue, jaw, teeth, lips and palate alter the air stream coming from your voice box. Articulation difficulties are usually characterized by substituting one sound for another (“wabbit” for “rabbit”), omitting a sound (“tar” for “star”) or distorting a sound (“ship” for “sip”).
What causes articulation problems?
Articulation problems may result from physical handicaps, such as cerebral palsy, cleft palate, or hearing loss, or may be related to other problems in the mouth, such as dental problems. However, most articulation problems occur in the absence of any obvious physical disability and are simply related to incorrect or delayed learning of speech sounds. See below for normal ages of learning sounds.
Can articulation problems be corrected?
Most articulation problems can be helped, however the longer the problem persists, the harder it is to change. Both children and adults can benefit from speech therapy.
How can a speech-language pathologist help?
Speech-language pathologists have a unique knowledge base of how speech sounds are produced. They are trained to assess and treat articulation difficulties and can help individuals speak more intelligibly by training the specific motor processes involved in planning and executing speech.
Is there anything I can try myself?
Try to repeat or imitate the problem sound after someone models it correctly. Use a mirror to examine what your tongue and lips are doing and see if you can change the pattern to look more like your model. Check with a speech-language pathologist if you need more assistance.
SPEECH SOUND DEVELOPMENT
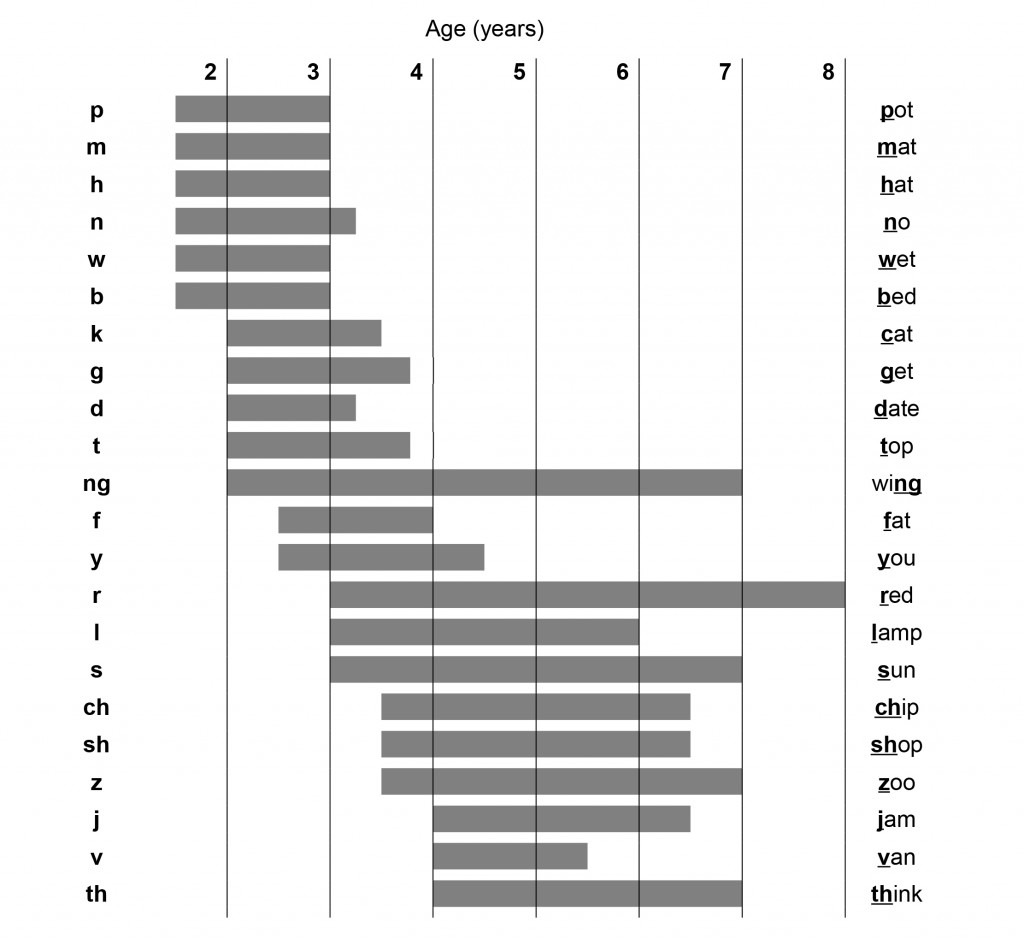
This chart represents combined data from Sander (1972), Grunwell (1981), Smit et al. (1990) and Williamson (2010). The left-hand edge of each horizontal bar represents the age at which 50% of children produce the particular consonant correctly and use it in their speech. The right-hand edge or each bar represents the age at which 90% of children have mastered the use of the consonant in their speech.
